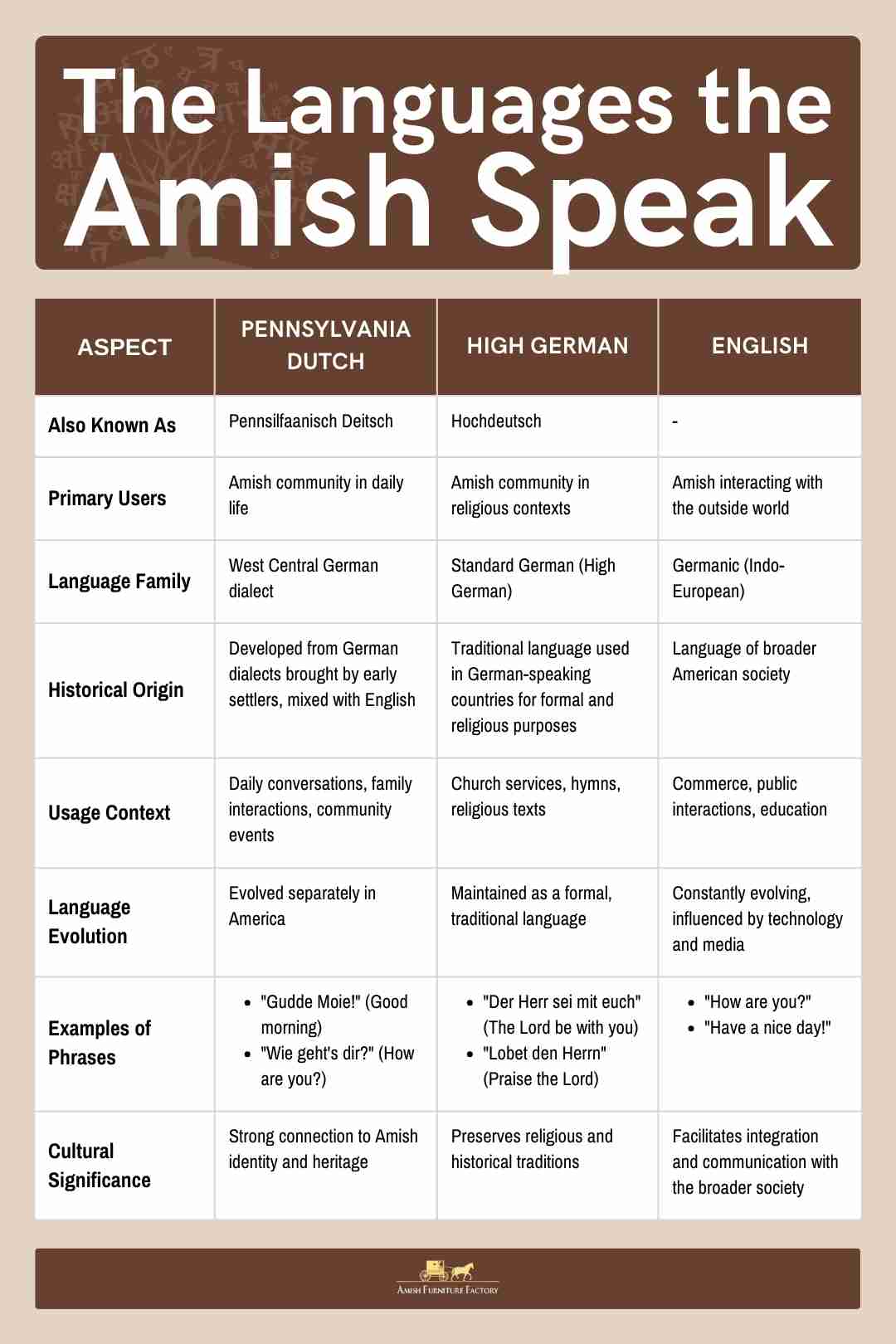
What secrets do the Amish people hold within their communities, particularly concerning the languages they embrace? The Amish, known for their distinct lifestyle and adherence to tradition, primarily communicate through a blend of Pennsylvania Dutch, English, and, in some cases, Alemannic dialects, creating a linguistic tapestry as unique as their culture itself.
The question of Amish language often sparks curiosity, especially among visitors to Amish communities. At the Amish Farm & House, it's one of the most frequently posed inquiries. Tourists often wonder if the Amish possess their own unique language, and if so, what it is. The answer isn't as straightforward as one might expect, revealing a complex interplay of languages that reflects their history and values. It is essential to understand how these languages function within the Amish community to truly appreciate their cultural identity.
The Amish, a group of Anabaptist Christians, are known for their simple living, traditional attire, and avoidance of modern technology. Their language use is a critical component of their cultural preservation. In Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, where a significant Amish population resides, Pennsylvania Dutch is a cornerstone of their daily communication.
The roots of Pennsylvania Dutch are deeply intertwined with the migration of German speakers to Pennsylvania during the 18th century. Approximately 81,000 individuals from central and southwestern Germany, Alsace, and Switzerland settled in the region, bringing with them their regional dialects. These dialects, which often differed from the emerging written German of the time, formed the basis of what is now known as Pennsylvania Dutch.
It is important to note that the term "Dutch" in "Pennsylvania Dutch" can be misleading. It's a mistranslation of the word "Deutsch," which is what the Amish originally called their Germanic language. Early American settlers may have confused this with the word "Dutch," which was used to describe people from both Germany and the Netherlands. Therefore, "Pennsylvania Dutch" is not a derivative of the Dutch language, but rather a dialect of German.
Pennsylvania Dutch remains a vibrant and integral part of Amish life. It is used in homes, community gatherings, and religious services. While English is increasingly utilized in interactions with the outside world, Pennsylvania Dutch serves as a critical element of internal communication and identity formation. The language allows them to maintain a sense of unity and cultural distinctiveness, reflecting their history and values.
Besides Pennsylvania Dutch, English plays a significant role in the Amish community. The Amish learn to read, write, and speak English, providing a crucial connection to the broader world. This allows them to engage in commerce, conduct business, and navigate the necessities of modern life. English is also the predominant language used in schools and interactions with non-Amish individuals.
In addition to Pennsylvania Dutch and English, some Amish communities use Alemannic dialects. This is particularly true among the Swiss Amish in Indiana. These dialects represent another layer of linguistic diversity within the Amish population.
The use of three distinct languages serves as a powerful symbol of Amish identity. Pennsylvania Dutch, English, and sometimes Alemannic dialects create a complex linguistic landscape that reinforces their cultural boundaries and preserves their heritage. The Amish have been able to maintain their language and culture by resisting assimilation and using the languages to communicate internally and externally.
The language is more than just communication; it is a reflection of the origins of the Amish. The heritage of the Amish can be seen in the roots of the Pennsylvania Dutch language, which has Swiss German and Alsatian influences. The language, like their traditional handwoven baskets, is woven into the fabric of daily life and practices.
As of 2024, the Amish population has surpassed 400,000, with about 395,000 residing in the United States and over 6,000 in Canada. This increase highlights the continued relevance and strength of Amish culture, including its linguistic traditions.
Learning about the language of the Amish provides a window into their world. The language allows one to better understand how the Amish live and communicate with the world. High school German classes can provide people with the chance to communicate with the Amish in one of their native languages.
There are instances where the language can differ within the Amish community. Some Amish groups have unique traditions and dialects, such as their folk music and yodeling songs.
The use of Pennsylvania Dutch, English, and sometimes Alemannic dialects by the Amish demonstrates their ability to preserve their cultural boundaries while interacting with the larger world. Their language, like the Amish themselves, is a story of resiliency, heritage, and community.
Many people are curious about the number of languages spoken by the Amish. The language spoken most commonly by the Amish is Pennsylvania Dutch, and also English. They have created a very distinct culture with the use of their languages.
In summary, the Amish population primarily speaks two languages: Pennsylvania Dutch and English. Pennsylvania Dutch serves as the first language, allowing them to communicate internally and preserve their heritage. The English language is essential for interactions with the outside world, facilitating their integration with the outside world. By understanding the role of Pennsylvania Dutch and English, one can gain a better insight into the Amish culture and way of life.
The Amish, like other communities, have a strong sense of identity. The preservation of their linguistic identity is a reflection of their commitment to their cultural values. They are able to preserve their traditions and culture by understanding the importance of language.
The primary language of the Amish is Pennsylvania Dutch. The language is related to standard German but has distinct grammar and pronunciation patterns. It is a vital component of the Amish's cultural identity and their ability to preserve their traditions. The dialects can vary. In addition to Pennsylvania Dutch, English is also commonly spoken, especially for interactions with the outside world.
The Amish community's linguistic landscape offers a fascinating glimpse into their cultural identity and historical development. By recognizing the role of Pennsylvania Dutch, English, and, at times, Alemannic dialects, one gains a deeper appreciation for the unique culture of the Amish. Their languages, like their culture, is an example of how language is used to uphold customs and traditions.